Search Results for: justice and security bill
27 March 2024 by Kate Litman
In UK News
On Tuesday the government published its response to the public inquiry into Brook House Immigration Removal Centre. The inquiry was a response to a 2017 investigative documentary, which included footage of staff abusing detained people. The inquiry’s report was published on 19 September 2023. In its response the government described the documentary footage as “utterly shocking”, but emphasised the fact that “[d]etention is and will remain a fundamental element of the immigration system”. The government rejected the report’s key recommendation that it should set a time limit on detention. The response sought to highlight changes that have been made across the immigration detention estate since the events of 2017, such as the improved ratio of custodial staff to detained persons and the introduction of accredited training and a code of conduct for staff. The government stated that a “comprehensive review” into complaints and whistle blowing processes is being undertaken.
In other news, a memorandum disclosed to the Afghanistan Inquiry shows that in 2011 a UK Special Forces commander raised concerns that “there is in effect an unofficial policy… to kill wherever possible fighting aged males on target, regardless of the immediate threat they pose to our troops. In some instances this has involved the deliberate killing [of] individuals after they have been restrained… and the subsequent fabrication of evidence to suggest a lawful killing in self-defence”. The inquiry is investigating alleged unlawful conduct by UK Special Forces in Afghanistan between 2010 and 2013 and the adequacy of the Ministry of Defence’s response to concerns that were raised at the time. Johnny Mercer MP, the Minister for Defence People and Veterans, has stated in his witness statement that he was shown a copy of the memorandum but not allowed to keep it. Mercer been ordered to disclose the names of those who told him about alleged war crimes to the inquiry.
In international news
The Hong Kong government passed new national security legislation known as ‘Article 23’. The new law increases prison sentences for national security related offences, including a maximum jail sentence of 10 years for sedition where an ‘external force’ is involved. Any speech which is critical of the government could potentially come under the scope of sedition, and Hong Kong’s justice minister has since stated that a person might commit an offence if they share criticism of the legislation online. The legislation gives the police the power to detain someone for 16 days without charge and to prohibit the person from consulting with a lawyer for 48 hours. UK Foreign Secretary David Cameron previously stated that the legislative proposals would “have a negative impact on the people of Hong Kong in the exercise of their rights and freedoms”. The EU has expressed concerns over the legislation’s ‘sweeping provisions and broad defintions’ and described the increased penalties, which have extraterritorial reach, as “deeply worrying”.
In the courts
The Court of Appeal ruled that an individual’s views on climate change do not form part of the ‘circumstances’ of criminal damage which is committed as part of a protest. Previously, climate protesters had successfully relied on the defence that they honestly believed the owner of the property would have consented to the damage if they had known of the damage “and its circumstances”. The Court emphasised that the “circumstances must belong to the damage, not to the defendant”, and that there “must be a sufficient connection between the damage and its circumstances”. The case under consideration involved a climate protester (“C”) who had caused damage to the offices of various charities and political parties. The court held that “what C had to say about the facts of or effects of climate change could not amount to the circumstances of the damage” and that such evidence would be inadmissible in relation to the consent defence.
Like this:
Like Loading...
18 September 2011 by Guest Contributor
 Updated |Nine years ago, in March 2002, Amanda “Milly” Dowler (aged 13) was on her way home from school. She was kidnapped and murdered and her body was found in September 2002. In June 2011, Levi Bellfield was convicted of her murder and sentenced to a “whole life” tariff. When Milly went missing, journalists of the News of the World newspaper “hacked” into her voicemail. The fact that this had happened came to public prominence in July 2011 when The Guardian newspaper revealed the story.
Updated |Nine years ago, in March 2002, Amanda “Milly” Dowler (aged 13) was on her way home from school. She was kidnapped and murdered and her body was found in September 2002. In June 2011, Levi Bellfield was convicted of her murder and sentenced to a “whole life” tariff. When Milly went missing, journalists of the News of the World newspaper “hacked” into her voicemail. The fact that this had happened came to public prominence in July 2011 when The Guardian newspaper revealed the story.
The Metropolitan Police are now seeking an order that The Guardian journalists reveal their sources of information about the hacking. There is a suggestion that the Official Secrets Act 1989 may have been breached. The Guardian plans to resist this “extraordinary demand to the utmost” – see The Guardian 17th September – “Hacking: Met use Official Secrets Act to demand Guardian reveals sources.”
Continue reading →
Like this:
Like Loading...
22 December 2021 by Jonathan Metzer
And so we come to the end of another year. The Covid-19 pandemic has continued to dominate the news, particularly with the very concerning surge of the Omicron variant this month. Many reading this will be separated from loved ones over Christmas. The year has also seen the return to power of the Taliban in Afghanistan after the US withdrawal at the end of August, the resumption of military rule in Myanmar and the ongoing persecution of the Uyghurs by the Chinese government, this year recognised by the House of Commons and the US government (as well as many other bodies and organisations) as constituting a genocide. So, one could say that this year has rivalled last year for infamy.
And yet, any year contains light as well as darkness. Also in 2021, researchers at Brown University successfully transmitted brain signals wirelessly to a computer for the first time (hopefully a breakthrough in treatment for paralyzed people), 124,000 new trees were planted in Sumatra as part of reforestation efforts, the WHO gave approval for widespread use of a groundbreaking malaria vaccine and almost nine billion Covid vaccinations have so far been administered worldwide since the first dose given in the UK 12 months ago, for a virus which only arrived 12 months before that.
But what, I hear you ask, about the law? As always, this year has been packed with fascinating and important legal developments — many of which you may have caught, but some of which may have passed under the radar. And so, please refresh your glass (or mug) and join me on another adventure as we review the 10 cases that defined 2021.
Continue reading →Like this:
Like Loading...
9 January 2023 by Lucy Stock
In the news:
- President Putin has ordered his troops in Ukraine to cease fire for 36 hours over Orthodox Christmas and has urged Ukrainian forces to do the same. However, the move was rejected by Kyiv, and the US state department, as a “cynical trap” and propaganda move. Putin announced the truce, to begin at noon 6 January 2023, after a call by Patriarch Kirill, leader of the Russian Orthodox Church.
- Ministers announced legislation that looks to enforce “minimum service levels” in six sectors, including the health service, rail, education, fire and border security. Unions that refuse to do so will face injunctions and could be sued for damages. Employers will be able to sue unions, and dismiss union members who are told to work under the minimum service requirement but refuse to do so. Prime minister Rishi Sunak, however, vetoed more far-reaching measures that would have increased the threshold for strike ballots, doubled the notice for industrial action from two weeks to a month, and banned ambulance workers from striking.
- The British Medical Association have informed the government that junior doctors will strike for 72 hours in March if the action is supported in a ballot opening next week. Doctors would not provide emergency care during the strike. The union, which has 45,000 junior doctor members, wants their real-terms pay restored to 2008 levels: a 26.1 per cent increase. The scale of the strike proposed by the BMA is larger than those to be held by nurses and ambulance staff, and will inflame tensions between the unions and the government. The Royal College of Nursing strikes are for 12 hours at a time, and the ambulance unions are holding 24-hour strikes.
Continue reading →Like this:
Like Loading...
25 March 2011 by Rosalind English
 The case of Patmainiece v Secretary of State for Work and Pensions was reported in an earlier post. Here we discuss the underlying rationale for the decision and ask whether the finding that the nationality requirement amounted to mere indirect discrimination was a correct “fit” with EU principles of free movement.
The case of Patmainiece v Secretary of State for Work and Pensions was reported in an earlier post. Here we discuss the underlying rationale for the decision and ask whether the finding that the nationality requirement amounted to mere indirect discrimination was a correct “fit” with EU principles of free movement.
Article 18 (now article 21 TFEU) provides:
1. Every citizen of the Union shall have the right to move and reside freely within the territory of the Member States
However a different regime applies to non-economic actors as opposed to workers. Free movement of workers is one of the fundamental underpinnings of the internal market on which the EU is based. The main EU Directives and Regulations giving effect to the right to free movement of workers are Regulation No 1612/68 on freedom of movement for workers within the Community (as amended by Directive 2004/38/EC) and Directive 2004/38/EC on the right of EU citizens and their family members to move and reside freely within the territory of the member states. But the rights of those who are economically inactive to reside for more than three months in other member states is subject to certain conditions, set out in the 2004 Directive; they must
Continue reading →
Like this:
Like Loading...
7 April 2011 by Adam Wagner
 BM v Secretary of State for the Home Department [2011] EWCA Civ 366 (05 April 2011) – Read judgment
BM v Secretary of State for the Home Department [2011] EWCA Civ 366 (05 April 2011) – Read judgment
Another control order has been ruled unlawful and quashed by the court of appeal, on the basis that the evidence relied upon to impose it was “too vague and speculative”.
Control orders are a controversial anti-terorrism instrument (see this post) which are soon to be replaced with Terrorism Prevention and Investigation Measures. These will impose less onerous restrictions upon a terrorist suspect. No doubt they will be approached by the courts at some stage. In the meantime, there are still 9 control orders in operation under the current regime. One has just been quashed by the court of appeal.
Continue reading →
Like this:
Like Loading...
12 March 2025 by Shaheen Rahman
N3 & ZA v Secretary of State for the Home Department [2025] UKSC 6 concerned orders depriving two British people of their citizenship on national security grounds. The Defendant (initially) contended that to do so would not render them stateless, because they were dual British Bangladeshi nationals.
The use of deprivation orders in this context has been controversial, with critics across the political spectrum. Notably, writing in the Spectator, Jacob Rees-Mogg said of the Shamima Begum case:
“The ability to deprive people, who have a claim to another citizenship, of their British passport, creates two categories of Briton. Those with no right to another nationality are in the first-class carriage. Whatever they do, they cannot be made an exile or outlaw and expelled from the country. On the other hand, those who themselves came to the UK or whose parents did so are in the second-class carriage. They may be stripped of their citizenship even if they have never claimed another foreign nationality or even visited the country. This is a fundamentally racist policy as it denies the absolute Britishness of all those who are either recent immigrants themselves or their children.”
In the instant case, the deprivation orders were subsequently withdrawn. The Supreme Court has held that the effect of that withdrawal is that the Appellants are to be treated as having been British Citizens throughout.
Continue reading →Like this:
Like Loading...
27 February 2023 by Hal McNulty
In the news
The UN General Assembly backed a resolution condemning Russia’s actions and calling for an end to the war on Thursday, the eve of the anniversary of the invasion. With 141 supporters, 32 abstentions and seven voting against, the resolution reiterated the UN’s support for Ukraine and called for a “comprehensive, just and lasting peace.” Abstentions included China, India and South Africa, while Russia, North Korea and Syria were among those voting against. General Assembly resolutions are not legally binding but carry great political weight, and the UN Security Council is obstructed from action by Russia’s veto. On the same day in Vienna, a large number of delegates walked out of a parliamentary assembly of the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) in protest against Austria’s decision to give visas to Russian officials.
Leading supermarkets in the UK have introduced customer limits on purchases of fruits and vegetables. According to the British Retail Consortium, the shortages are expected to last a few weeks until reliance on imports from Spain and north Africa is counteracted by the start of the UK growing season. Tom Bradshaw, one of the leaders of the National Farmers’ Union (NFU), has called for the UK to “take command” of its supply chains. Citing Brexit, the Ukraine War, and climate change, the NFU wants the government to use the powers granted it by the Agriculture Act 2020 to address exceptional market conditions.
Continue reading →Like this:
Like Loading...
17 June 2019 by Conor Monighan
Conor Monighan brings us the latest updates in human rights law

Credit: The Guardian
In the News:
The High Court has heard how MI5, which is responsible for domestic spying operations, may have unlawfully retained the data of innocent civilians for years.
Liberty’s challenge centres on the Investigatory Powers Act 2016, which gives the security services the ability to access digital devices and electronic communications. It alleges that the system of information gathering used by the security services is illegal.
As part of a systemic judicial review, the High Court was told MI5 had realised that there were problems with their data handling in January 2016, but that the Prime Minister and Home Secretary were only informed in April. It was also alleged that MI5 has been holding sensitive data without proper safeguards. Liberty argued that the security services had submitted warrant applications which misled judges, because the agencies had incorrectly suggested sensitive data was being properly protected.
Much of the case will be heard in private over the next week.
In Other News….
Continue reading →
Like this:
Like Loading...
6 May 2025 by Rebecca Ebner-Landy
In UK News
The UK’s first transgender judge, Victoria McCloud, is bringing an action against the UK to the European Court of Human Rights over the Supreme Court’s ruling on biological sex in For Women Scotland Ltd v The Scottish Ministers [2025] UKSC 16. Lord Hodge, in this case, determined that the “unanimous decision of this court is that the terms woman and sex in the Equality Act 2010 refer to a biological woman and biological sex”. McCloud – one of at least two individuals who had unsuccessfully sought leave to intervene in the proceedings – is bringing the action on grounds that her Article 6 rights, which guarantee the right to a fair trial, have been infringed. She argues that the Supreme Court refused to hear her evidence about the “impact of those trans people affected by the judgement” and failed to “give any reasons” for doing so. Further, in her submission, the court had not considered human rights arguments that “would have been put by trans people” leaving her with the “nonsense” of being “two sexes at once”. In contrast, the court had heard from “protest groups speaking on behalf of women” in the case. McCloud is now seeking a declaration that “the actions of the UK government and the Supreme court judgement violate her fundamental human rights”.
In an amendment to the Border, Security, Asylum and Immigration Bill which is being considered by Parliament, the Home Office seeks to ban foreign sex offenders from claiming asylum in the UK. The amendment would affect anyone who qualifies for sex offender status. Under Article 1F of the Refugee Convention 1951 countries are entitled to refuse asylum to terrorists, war criminals and individuals convicted of a particularly serious crime who present a danger to the community. Where a conviction qualifies a foreign national for the sex offenders’ register – regardless of the length of sentence they receive – that will lead to their refugee status being denied, on the basis that they will be presumed to have been convicted of a “particularly serious crime” . The Government has said that they are “toughening [their] approach to border security through stricter enforcement of the rules”, in an attempt to make “Britain’s streets safer”. Specifically, Home Secretary Yvette Cooper has argued the amendment would ensure these “appalling crimes are taken seriously”. Steve Valdez-Symonds, at Amnesty International UK, however, has raised concerns that the Government is “rushing through late-stage amendments” to major legislations meaning that “laws are made without the full scrutiny and care they demand”. In his opinion this is an “irresponsible approach” to lawmaking.
Continue reading →Like this:
Like Loading...
1 February 2021 by Byul Ryan-Im
In the news:
The week began with the first Opposition Day of 2021, with Labour choosing to put council tax and employment rights centre of the Parliamentary stage. This followed an admission last week by Business Secretary Kwasi Kwarteng that the government was reviewing certain workers’ rights which had been saved post-Brexit as retained EU employment law. Responding to allegations that the government planned to scrap the 48-hour maximum work week and change the rules around rest breaks and holiday pay calculation, he tweeted ‘[w]e are not going to lower the standards of workers’ rights’. During the Opposition Day Debate Mr Kwarteng confirmed the review was no longer happening and that the government would not row back on the 48-hour work week, annual leave entitlement or rest breaks at work.
Continue reading →Like this:
Like Loading...
31 January 2019 by Guest Contributor
Domestic abuse is endemic in UK society. The law’s response has consisted of sporadic police prosecutions, a Protection from Harassment Act 1997 (rarely used), and uncoordinated remedies in family proceedings mostly under Family Law Act 1996 Part 4 (the non-molestation and the occupation order). Each is governed by a different set of procedural rules; and different means of enforcement. Views vary as to what is the legal definition of ‘domestic violence’ – still used by the Legal Aid Agency: see Legal Aid Sentencing and Punishment of Offenders Act 2012 – and ‘domestic abuse’, which is now defined by a family proceedings practice direction which deals only with children proceedings (yes, really): Family Procedure Rules 2010 PD12J.
Probably the only definition in law (as opposed to a Practice Direction) is still that of Lord Scarman in Davis v Johnson[1978] UKHL 1, [1979] AC 264 at 276 where of the then Domestic Violence and Matrimonial Proceedings Act 1976 he said:
I conclude that the mischief against which Parliament has legislated by … the Act [there was no definition in the 1976 Act] may be described in these terms: conduct by a family partner which puts at risk the security, or sense of security, of the other partner in the home. Physical violence, or the threat of it, is clearly within the mischief. But there is more to it than that. Homelessness can be as great a threat as physical violence to the security of a woman (or man) and her children….’. I suspect that definition – though it should be – is rarely cited. (Davis v Johnsonremains important: it provides the continuing House of Lords definition of the stare decisisrule.)
Continue reading →Like this:
Like Loading...
3 June 2020 by Michael Spencer
R (W, a child) v Secretary of State for the Home Department, Project 17 intervening [2020] EWHC 1299
Does the common law protect the right of foreign residents to relief from destitution?
In this judgment on the Home Secretary’s “no recourse to public funds” (NRPF) policy, the Divisional Court of the Queen’s Bench Division has confirmed that it does, citing authority going back to the time of the poor laws.
The judgment will come as a welcome relief to migrants with human rights visas who may be struggling in the wake of the Covid-19 pandemic. It also provides insight into the interaction between the common law and the Human Rights Act 1998.
Continue reading →Like this:
Like Loading...
14 October 2010 by Rosalind English
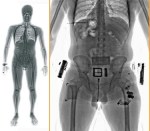 Full body scanners are to become the only security option for people flying out of Manchester Airport, the BBC reports today. The excessive amount of coverage given to the disapproval expressed by civil liberties groups has now been counterbalanced by passengers’ attitudes, since it appears that people actually prefer the scanners to the full body pat down, and have been voting with their feet.
Full body scanners are to become the only security option for people flying out of Manchester Airport, the BBC reports today. The excessive amount of coverage given to the disapproval expressed by civil liberties groups has now been counterbalanced by passengers’ attitudes, since it appears that people actually prefer the scanners to the full body pat down, and have been voting with their feet.
According to Manchester Airport, 95% of travellers prefer the scanners and queuing times have been radically reduced. It takes 2 minutes to undergo a pat down, but a mere 27 seconds to pass through a scanner.
Continue reading →
Like this:
Like Loading...
1 May 2020 by Rafe Jennings
Latest news: GCHQ has published a detailed blog article which seeks to explain (and defend) the new NHS contact tracing app, which the Government regards as the key to a controlled exit from lockdown.
Coronavirus presents a serious threat to society, legitimising the collection of public health data under Article 9:2 (g) of GDPR regulations, which allows the processing of such data if “necessary for reasons of substantial public interest”. Some of this collection will take the form of contact tracing apps, which have been used in containing the spread of coronavirus in countries such as Singapore.
They work by broadcasting a bluetooth signal from a smartphone which is picked up by other smartphones (and vice versa), meaning that if one user contracts coronavirus, those who have been in contact with that user can be effectively warned and given further advice to stop the spread.
NHSX, the body responsible for setting NHS data usage policy and best practice, has been developing a contact tracing app which is currently undergoing effectiveness trials at RAF Leeming. As it stands, the app either tells you “You’re okay now” or “You need to isolate yourself and stay at home”. It seems likely that this or a similar app will be rolled out over the UK in the coming months.
Continue reading →Like this:
Like Loading...




 BM v Secretary of State for the Home Department [2011] EWCA Civ 366 (05 April 2011) –
BM v Secretary of State for the Home Department [2011] EWCA Civ 366 (05 April 2011) –



Recent comments